We have moved!
We are pleased to announce that our registered office has officially moved to a new location. Our new address is:
Sjögren's UK, Hastingwood Business Park, Wood Lane, Erdington, Birmingham, B24 9QR.
All other contact information including our phone number and email, will remain the same. We look forward to welcoming you to our new space and continuing to serve you with the same dedication and quality you expect from us.
Understanding the Diagnostic Process
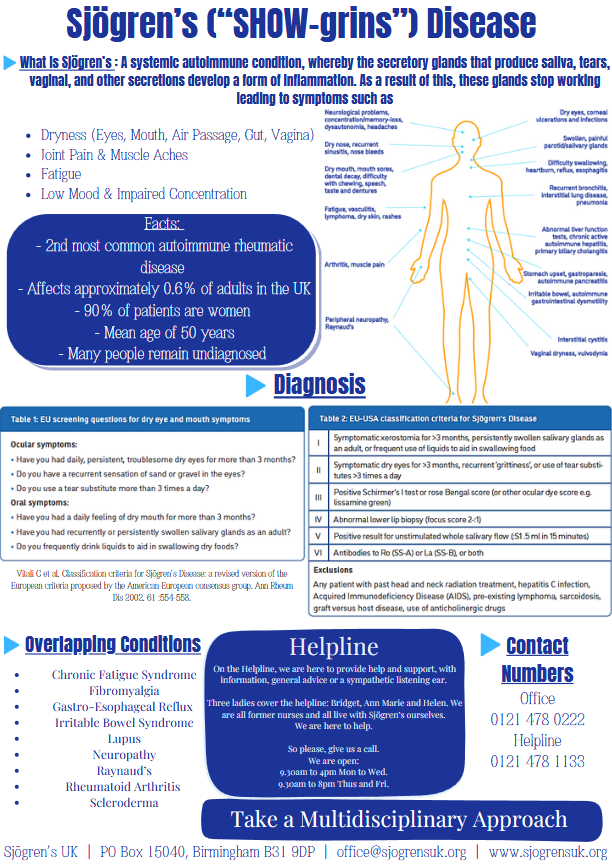
Sjögren’s can be a challenging condition to diagnose due to its complex nature and overlapping symptoms. Symptoms often mimic those of other conditions, such as menopause, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, fibromyalgia, chronic fatigue syndrome, or multiple sclerosis. This overlap can make it difficult to promptly identify Sjögren’s as the underlying cause.
Additionally, patients often present symptoms that are treated in isolation, leading to a fragmented approach. For example, an ophthalmologist may treat persistent dry eye without recognizing systemic symptoms, or a general practitioner may address joint pain without considering dryness or fatigue.

Timely and accurate diagnosis is critical to improving patient outcomes and quality of life. Diagnosing Sjögren’s requires a combination of clinical evaluations, patient history, and specialized tests. Rheumatologists typically play a central role in diagnosing and managing the condition, while ophthalmologists and oral medicine specialists often contribute key findings through focused assessments.
Resources for Medical Professionals
We are committed to supporting healthcare providers in recognizing and diagnosing Sjögren’s. Explore our resources designed to make the diagnostic process clearer and more efficient:
Concise Guide for Medical Professionals
Our guide offers information on:
- Principles of Diagnosis
- Role of Secondary Care
- Principles of Treatment
- Algorithm for diagnosis and treatment
Sjögren’s Disease Guidelines – British Society of Rheumatology (BSR)
The BSR have released an updated and expanded guideline providing evidence-based recommendations for the management of adult and juvenile onset Sjögren’s disease
Information Pack
Our comprehensive information pack is designed to detail the common symptoms and care of Sjögren’s in clear, patient-friendly language, including:
Request a Physical Copy
If you prefer a printed version of the Concise Guide, Information Pack or Flyer for yourself or someone else, we’d be happy to post it.
Contact us at office@sjogrensuk.org or 0121 478 0222 to request your copy.
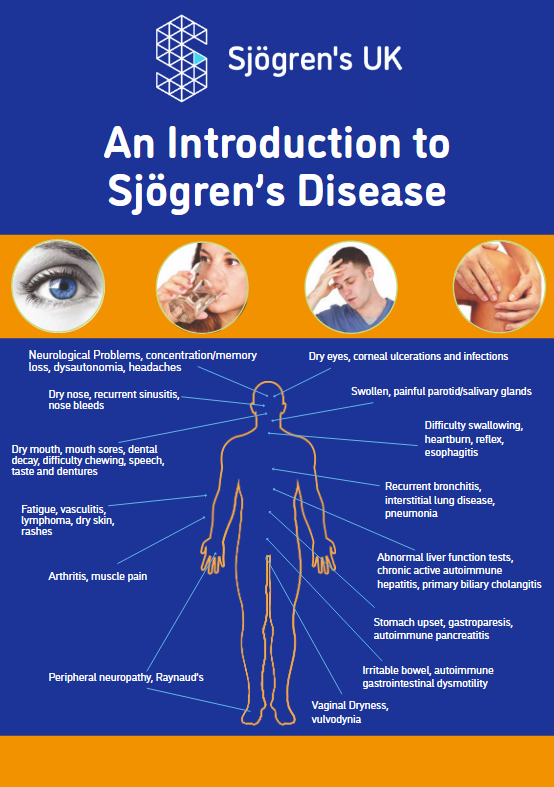
Overlapping Conditions
Sjögren’s often coexists with or mimics symptoms of other autoimmune and chronic conditions.
These include, but not limited to:
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Digestive Disorders
- Fibromyalgia
- Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux
- Gynaecological Disease
- Lupus
- Neuropathy
- Raynaud’s Rheumatoid
- Arthritis
- Scleroderma
- Skin dryness
- Thyroid Disease
It’s essential to differentiate Sjögren’s from these conditions or recognize when they occur together.
Accurate diagnosis can lead to more targeted treatment and improved outcomes.
Recognizing Flare-Ups and Their Role in Diagnosing Sjögren’s
Sjögren’s symptoms can fluctuate, with periods of heightened intensity (flare-ups) followed by times when symptoms seem to subside or become less noticeable. This episodic nature can make diagnosing Sjögren’s particularly challenging for healthcare professionals.
Why Flare-Ups Matter in Diagnosis
Inconsistent Symptom Presentation: A patient may appear relatively well during a clinical visit but report severe symptoms at other times. This can lead to underestimating the impact of the disease or misattributing symptoms to other conditions.
Overlapping Symptoms: Flare-ups often bring heightened fatigue, joint pain, and dryness, which overlap with many other conditions, complicating the diagnostic process.
Missed Opportunities: If healthcare professionals are unaware of symptom variability, they may miss crucial diagnostic cues during a “quiet” phase of the disease.
Key Tips for Healthcare Professionals
Listen to the Patient’s History: Encourage patients to describe their symptoms over time, not just what they are experiencing during the visit. A detailed symptom diary can be invaluable.
Consider Fluctuations: Be mindful that symptoms may appear mild during an evaluation but could significantly worsen during a flare-up.
Request Specialist Input: Symptoms like dry eye or oral dryness might be evaluated by eye care providers or dentists, while systemic issues might require a rheumatologist’s expertise.
Why Flare-Ups Matter in Diagnosis
Supporting Your Patients Understanding the unpredictable nature of Sjögren’s can foster empathy and a stronger doctor-patient relationship.
Encourage patients to:
- Track symptoms using a diary or app.
- Communicate any changes or patterns in their symptoms.
- Seek support from healthcare providers during flare-ups.
By recognizing and accounting for the variability in Sjögren’s symptoms, healthcare professionals can improve the diagnostic process, provide more personalised care, and help patients feel understood and supported.
Useful Webinars
Here are some webinars providing valuable insights into the diagnosis and symptom management for Sjögren’s:
“Looking After Yourself: Practical Self-Management Strategies” by Dr. Elizabeth Price, Rheumatologist at NHS Great Western Hospital & BSSA Medical President
“Fatigue in Sjögren’s” by Prof. Wan-Fai Ng, Professor of Rheumatology, Newcastle University, with Sjögren’s Europe & BSSA
“Rheumatology Roundtable: Sjogren disease guideline” by British Society for Rheumatology
Recognising the Broader Impact
Living with Sjögren’s goes beyond physical symptoms; it also takes a toll on patients’ mental and emotional well-being. Persistent symptoms like fatigue, chronic pain, and dryness can lead to feelings of frustration, isolation, and mental exhaustion. As healthcare professionals, understanding the psychological challenges faced by those living with Sjögren’s is vital. A holistic approach to care, one that acknowledges both the physical and emotional impacts, can help build trust with patients, improve their overall well-being, and ensure a more comprehensive approach to management.
Common Myths
Myth: Sjögren’s is a rare disease.
Fact: Sjögren’s is the 2nd most common rheumatic autoimmune disease, yet it is often underdiagnosed.
Myth: Only older women get Sjögren’s.
Fact: While it is more common in postmenopausal women, Sjögren’s can affect men, younger adults, and even children.
Myth: If standard tests are negative, you don’t have Sjögren’s.
Fact: Diagnosis often requires a combination of symptoms, specialized tests, and expert evaluation; standard tests alone may not capture all cases.
Myth: Sjögren’s symptoms are the same for everyone.
Fact: Symptoms vary widely between individuals, from mild dryness to severe systemic complications.
Myth: You can’t live a full life with Sjögren’s.
Fact: Many people with Sjögren’s manage their symptoms effectively through treatment, lifestyle adjustments, and support networks.
Myth: Sjögren’s doesn’t affect mental health.
Fact: Chronic symptoms like pain, fatigue, and isolation can lead to significant emotional challenges, including depression and anxiety.
Myth: Sjögren’s isn’t treatable.
Fact: While there is no cure, treatments are available to manage symptoms and improve quality of life, especially when diagnosed early.